棉花GhLSM1B基因在提高棉花组织培养时的愈伤组织增殖速率中的应用
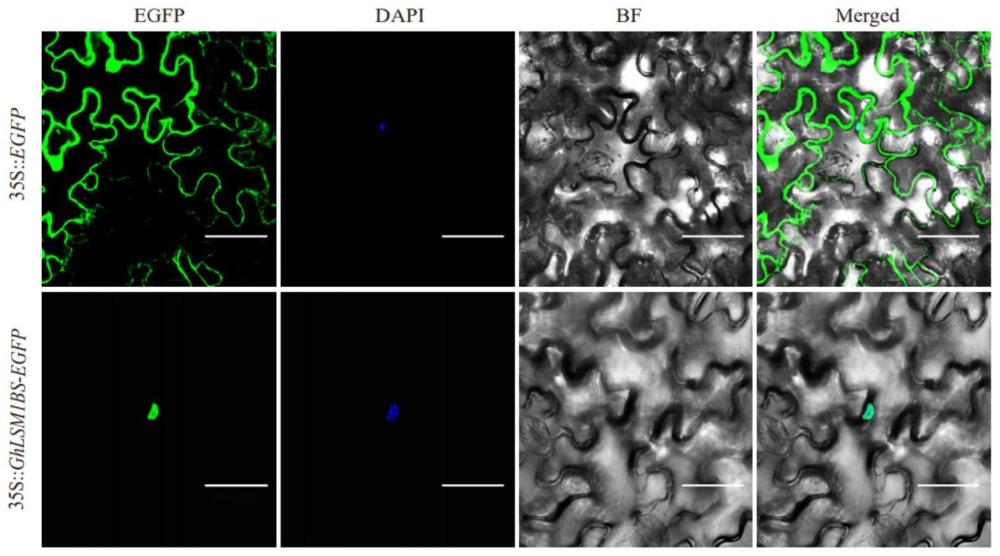
本发明属于基因工程领域,具体涉及棉花ghlsm1b基因在提高棉花组织培养时的愈伤组织增殖速率中的应用,以及一种提高棉花愈伤组织增殖速率的方法。
背景技术:
1、棉花是世界上重要的经济作物,也是天然纤维的主要来源(yao m.the situationand task of chinese cotton textile industry[j].cotton textile technology,2009,37(3):1-3)。棉花生产关乎国家的战略发展,提高棉花的产量和品质、增强棉花的抗逆和抗病等性状非常重要。然而,传统育种方法往往具有周期长、不确定性高、操作困难等缺陷。利用基因工程育种技术,可获得定向变异且育种周期更短,在改良棉花抗病、抗虫、纤维品质和纤维产量等性状中发挥重要作用(wilkins t a,rajasekaran k,anderson dm.cotton biotechnology[j].critical reviews in plant sciences,2000,19(6):511-550)。
2、体细胞胚胎发生是植物体细胞经过脱分化和再分化形成胚胎,而后发育成新的植株的无性繁殖过程(yang x,zhang x.regulation of somatic embryogenesis in higherplants[j].critical reviews in plant sciences,2010,29(1):36-57)。体细胞胚胎发生通常有两种方式,包括直接方式和间接方式(前者是指由外植体直接产生胚状体;后者是指通过去分化诱导体细胞形成愈伤组织,而后通过诱导愈伤组织再分化形成胚性愈伤组织和体细胞胚胎(yang x y,zhang x l,yuan d j,et al.transcript profiling revealscomplex auxin signalling pathway and transcription regulation involved indedifferentiation and redifferentiation during somatic embryogenesis incotton[j].bmc plant biology,2012,12:19)。目前,通过直接体细胞胚胎发生的方法获得棉花转基因植株的报道较少(nobre j,keith d j,dunwell j m.morphogenesis andregeneration from stomatal guard cell complexes of cotton(gossypium hirsutuml.)[j].plant cell reports,2001,20(1):8-15),大多数转基因棉花均是通过间接方式获得(rao a q,irfan m,saleem z,et al.overexpression of the phytochrome b genefrom arabidopsis thaliana increases plant growth and yield of cotton(gossypium hirsutum)[j].journal of zhejiang university-science b,2011,12(4):326-334;hao j,chen s,tu l l,et al.ghh2a12,a replication-dependent histone h2agene from gossypium hirsutum,is negatively involved in the development ofcotton fiber cells[j].plant cell reports,2014,33(10):1711-1721;guo q,meng s,tao s c,et al.overexpression of a samphire high-affinity potassiumtransporter gene sbhkt)。尽管基因工程育种已大大缩短了棉花育种的时长,棉花的遗传转化仍面临转化周期长、转化效率低、受基因型限制和畸形胚发生率高等问题(li j y,wang m j,li y j,et al.multi-omics analyses reveal epigenomics basis forcotton somatic embryogenesis through successive regeneration acclimationprocess[j].plant biotechnology journal,2019,17(2):435-450)。因此,解析棉花体细胞胚胎发生过程中的关键调控因子,对于提高棉花遗传转化效率具有重要意义。目前,已有一些研究报道了参与调控棉花体细胞胚胎发生的基因,如蛋白激酶类基因(min l,hu q,liy y,et al.leafy cotyledon1-casein kinase i-tcp15-phytochrome interactingfactor4 network regulates somatic embryogenesis by regulating auxinhomeostasis[j].plant physiology,2015,169(4):2805-2821;liu z j,zhao y p,zeng lh,et al.characterization of ghserk2 and its expression associated withsomatic embryogenesis and hormones level in upland cotton[j].journalofintegrative agriculture,2018,17(3):517-529mizna,moon s,sameera h,etal.embryogenic capabilities of cotton through tissue culture and expressionanalysis ofserk3 for regeneration potential[j].indian journal of agriculturalresearch,2020,54(3):361-366)、转录因子类基因(deng j w,sun w n,zhang b y,etal.ghtce1-ghtcee1 dimers regulate transcriptional reprogramming during wound-induced callus formation in cotton[j].plant cell,2022,34(11):4554-4568;hu ls,yang xy,yuan d j,et al.ghhmgb3 deficiency deregulates proliferation anddifferentiation of cells during somatic embryogenesis in cotton[j].plantbiotechnology journal,2011,9(9):1038-1048;xiao y q,chen y l,ding y p,etal.effects of ghwus from upland cotton(gossypium hirsutwn l.)on somaticembryogenesis and shoot regeneration[j].plant science,2018,270:157-165)以及激素合成和信号转导类基因(xu j,yang x,li b,et al.ghl1l1 affects cell fatespecification by regulating ghpin1-mediated auxin distribution[j].plantbiotechnology journal,2019,17(1):63-74.;li m f,wrobel-marek j,heidmann i,etal.auxin biosynthesis maintains embryo identity and growth during baby boom-induced somatic embryogenesis[j].plant physiology,2022,188(2):1095-1110)。然而,仍有大量参与体细胞胚胎发生的基因尚未被发现。
技术实现思路
1、本发明目的是明确ghlsm1b基因在调控棉花体细胞胚胎发生中的应用。本发明创制了过表达ghlsm1b基因的棉花材料,该材料愈伤组织生长加快;本发明探究了ghlsm1b基因在棉花体细胞胚胎发生中的基因功能,ghlsm1b基因促进该材料愈伤组织生长、造成该材料愈伤细胞体积增大。
2、本发明提供了ghlsm1b基因在提高棉花组织培养时的愈伤组织增殖速率中的应用,所述ghlsm1b基因为seq id no.1所示序列编码的基因。通过ghlsm1b基因过表达的棉花材料,其愈伤组织增殖速率大大提高。
3、本领域的普通技术人员可采用已知方法,对本发明中ghlsm1b基因的核苷酸序列进行突变,那些经过人工修饰后得到的具有与本发明基因ghlsm1b的核苷酸序列75%或是更高同一性的核苷酸,只要编码ghlsm1b基因且具有ghlsm1b基因的功能,均是衍生于本发明的核苷酸序列且等同于本发明的序列。
4、本发明首先提供一种所述ghlsm1b基因在提高棉花组织培养时的愈伤组织增殖速率中的应用。
5、本发明因而也提供一种提高棉花愈伤组织增殖速率的方法,其包括如下步骤:将所述ghlsm1b基因在棉花中进行过表达获得ghlsm1b基因过表达棉花材料,以所述ghlsm1b基因过表达棉花材料的部位作为外植体,进行愈伤组织的诱导步骤。任选地,还包括不定芽诱导、不定根的诱导和植株再生的步骤。
6、其中,所述ghlsm1b基因编码了seq id no.2所示的氨基酸序列。优选地,所述ghlsm1b基因的核苷酸序列为seq id no.1所示。
7、所述外植体是棉花无菌苗的下胚轴,优选地切成长约1cm的小段作为外植体。
8、所述棉花是陆地棉。
9、诱导愈伤组织时的培养基采用改良后的msb培养基。
10、诱导培养的条件是温度为27℃、相对湿度为65%的光照培养室中,光照周期为16h光照、8h黑暗,培养时长20-40d。
11、本发明提供了ghlsm1b基因在棉花ghlsm1b基因在提高棉花组织培养时的愈伤组织增殖速率中的应用,并同时提供提高棉花愈伤组织增殖速率的方法,其原理在于所述基因对棉花体细胞胚胎发生起作用,进而可以用于组织培养以及棉花再生中的应用,本发明获得的愈伤组织增殖率较野生型提高15%-69%。本发明成果可应用于调控棉花的体细胞胚胎发生效率和提高组织培养效率,因而有利于棉花的再生和转基因棉花的制备。
- 还没有人留言评论。精彩留言会获得点赞!